On July 1, a joint research team from Samsung Advanced Research Institute and Seoul National University published their latest Micro LED research results in the international academic journal Nature. They successfully developed a high-efficiency red InGaN-based Micro LED with a diameter of 1.5 micrometers, a peak external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 6.5%, a peak wavelength of 649nm, and flexible characteristics. This breakthrough can overcome the key bottlenecks in the miniaturization and high-definition display of AR, VR and other metaverse devices.

Photoluminescence (PL) and electroluminescence (EL) of red nano-LEDs with different ALD passivation layers (Image source: NATURE)
The research team employed a 1nm thick epitaxial aluminum nitride (AlN) passivation layer technique, using argon plasma-assisted atomic layer deposition (ALD) to form a single-crystal AlN thin film on the sidewalls of Micro LEDs. This ultrathin passivation layer effectively reduces non-radiative recombination, solving the problem of a sharp drop in efficiency in traditional red Micro LEDs caused by size reduction (<5 micrometers). Comparative experiments show that this technology increases photoluminescence intensity by 2.5 times and extends the light decay time by 4 times, far exceeding the performance of traditional hafnium dioxide (HfO₂) or aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) passivation layers.
To achieve flexible Micro LED displays, the research team flip-chip bonded a Micro LED array to a polyimide (PI) substrate. By controlling the interface adhesion force, they achieved non-peeling removal of the silicon substrate, ultimately obtaining a flexible device with a thickness of less than 20 μm. Test results show that this flexible red Micro LED maintains stable light emission even when bent, exhibiting good brightness uniformity.
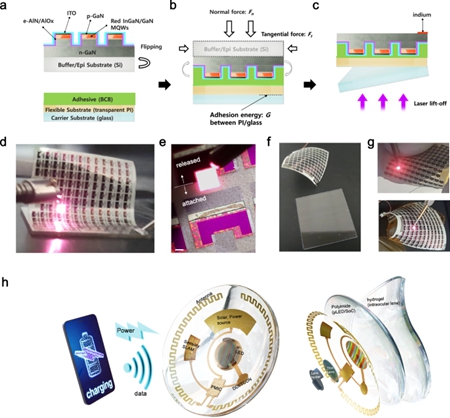
Device transfer of flexible e-AlN passivated red Micro LED (Image source: NATURE)
The research team stated that this achievement overcomes the limitations of efficiency, size, and rigid substrates in red Micro LEDs. Its 1.5μm emission size and 6.5% EQE meet the requirements for ultra-high density (>5000ppi) displays, making it applicable to next-generation devices such as AR glasses and even electronic contact lenses. In the future, by optimizing the indium gallium nitride epitaxial layer and integrated driving circuitry, it is expected to further improve efficiency uniformity, promoting the commercialization of full-color flexible Micro LED displays. (Compiled)


